The more liquid refrigerant that flashes to a vapor, the less liquid is left to absorb this heat energy. Less flash gas equals a higher net refrigerating effect and a more efficient system. Many designers reduce the amount of flash gas by additionally subcooling the liquid refrigerant entering the metering device
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the technology of indoor and vehicular environmental comfort. ... HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics and heat transfer. All About HVAC system.
Saturday, September 29, 2018
Thursday, September 27, 2018
HVAC PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE CHECKLIST
HVAC PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE CHECKLIST
OUTDOOR UNITS
- Inspect unit for proper refrigerant level and adjust if necessary
- Clean dirt, leaves and debris from inside cabinet
- Inspect base pan for restricted drain openings—remove obstructions as necessary
- Inspect coil and cabinet—clean as needed
- Inspect fan motor and fan blades for wear and damage—on older models lubricate as needed
- Inspect control box, associated controls/accessories, wiring and connections. Controls may include contactors, relays, circuit boards, capacitors, sump heat and other accessories. All control box and electrical parts should be checked for wear or damage.
- Inspect compressor and associated tubing for damage
- INDOOR UNITS
- Inspect and clean blower assembly (includes blower housing, blower wheel and motor)
- On older models, lubricate motor and inspect and replace fan belt if needed
- Check combustion blower housing for lint and debris and clean as necessary
- Inspect evaporator coil, drain pan and condensate drain lines. Clean as needed
- Inspect for gas leaks in gas furnaces
- Inspect burner assembly—clean and adjust as needed
- Inspect ignition system and safety controls—clean and adjust as needed
- Inspect heat exchanger or heating elements
- Inspect flue system—check for proper attachment to the furnace, any dislocated sections, and for signs of corrosion. Replace if necessary.
- Inspect control box, associated controls, wiring and connections
- Clean or replace air filters
- Inspect conditioned airflow system (ductwork)—check for leaks
- Monitor system starting characteristics and capabilities
- Listen for abnormal noise
- Search for source of unusual odors
- Monitor air conditioning and heat pump systems for correct refrigerant charge
- Measure outdoor dry bulb temperature
- Measure indoor dry and wet bulb temperature
- Measure high and low side system pressures
- Monitor gas furnace for correct line and manifold gas pressure—make adjustments as needed
- Measure temperature rise and adjust airflow as needed
- Check vent system for proper operation
- Monitor system for correct line and load volts/amps
- Monitor system operation per manufacturer’s specifications
- Provide system operation report and recommend repairs or replacement as necessary.
- COOLING SYSTEM MAINTENANCE
- Set the thermostat as high as comfort will permit.
- Make sure attics are adequately ventilated to relieve heat buildup. If necessary, improve airflow by adding or enlarging vents.
- When building a new house or renovating an old one, choose light-colored roof shingles to reflect more of the sun’s heat.
- During moderate weather, don’t use the air conditioner unnecessarily.
- Draw blinds or drapes to block the sunlight during the hottest part of the day.
- Install awnings over windows exposed to direct sunlight.
- In the cooling season, don’t run kitchen and bath exhaust fans longer than necessary.
- Don’t place lamps, TV sets or other heat-producing devices beneath a wall-mounted thermostat. Rising heat from that equipment may cause the air conditioning system to overcool your house.
- HEATING & FURNACE MAINTENANCE
- Locate the thermostat on an inside wall away from windows and doors.
- Set the thermostat as low as comfort permits. Each degree over 68°F can add 3% to the amount of energy needed for heating.
- People generate heat. So lower the thermostat a degree or two when expecting a large group of guests.
- INSULATION
- Make sure your home is properly insulated. This is the single most important step in conserving energy. Thermal insulation should be specified in terms of thermal resistance (R-values). R-30 (10″) is recommended for ceilings, and R-11 (3-1/2”) for exterior walls and floors over unheated areas. In colder climates, consider additional insulation.
- Infiltration of humid outside air is your heating and air conditioning system’s worst enemy—it could account for 15% to 30% of air conditioning energy requirements. Find the places where air can sneak into the home and plug them with caulking, weather-stripping or plastic. Also, weather-strip and caulk around all entrance doors and windows.
- Cut heat transfer through your windows by 40% to 50% with double-glazing (two panes of glass separated by a sealed air space) and low-e glass.
- Use wood- or metal-frame storm windows even if single-glazed windows are high quality. The extra layer of glass and the layer of still air will cut heat transfer considerably.
- Install storm doors at all entrances to your house.
- Keep all windows and doors closed.
- Remember that by increasing the glass area, you increase the amount of heat added in summer and lost in winter.
- Make sure fireplaces have tight-fitting dampers, which can be closed when the fireplace is not in use. Invest in a humidifier to conserve energy in winter. The air in your home won’t be as dry, so you stay comfortable at a lower temperature setting.
HVAC MAINTENANCE TIPS
HVAC MAINTENANCE TIPS
Inspect, Clean, or Change Air Filters Once a Month
Change your filters often in your central air conditioner, furnace, and/or heat pump. A dirty filter can increase energy costs and damage your equipment, leading to early failure
Schedule Seasonal HVAC Maintenance
Have annual system maintenance service performed one to two months before the summer season begins. Research shows that keeping your system clean and running effectively can save you over 20% on your heating and cooling costs
Clear the area around your HVAC system
Keep the condensing unit free of debris. Trim shrubs and plants near your air conditioning unit to ensure proper air flow and circulation
Clean Evaporator and Condenser Coils (once or twice a year)
The U.S. Department of Energy says that “a dirty condenser coil can increase energy consumption by 30%
Maximize Air Flow
Clean your vents and registers at least annually to help them circulate air as efficiently as possible
Install a Programmable Thermostat
Programmable thermostats can be programmed to change the temperature while you’re away or sleeping and can cut an energy bill by at least 10%
Tuesday, September 25, 2018
HVAC Compressors
''The system refrigerant starts its cycle in a gaseous state. The compressor pumps the refrigerant gas up to a high pressure and temperature. From there it enters a heat exchanger (sometimes called a condensing coil or condenser) where it loses energy (heat) to the outside, cools, and condenses into its liquid phase''
A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor.
Compressors are similar to PUMP: both increase the pressure on a fluid and both can transport the fluid through a pipe. As gases are compressible, the compressor also reduces the volume of a gas. Liquids are relatively in compressible; while some can be compressed, the main action of a pump is to pressurize and transport liquids.

There are basically 5 types of air conditioner compressor that are commonly used in the HVAC industry:
- Reciprocating.
- Scroll.
- Screw.
- Rotary.
- Centrifugal.
There are basically 5 types of air conditioner compressor that are commonly used in the HVAC industry:
Reciprocating Air Conditioner Compressor
The reciprocating compressor uses piston to compressor the refrigerant driven by a crankshaft in a straight line back and forth motion. This rotary motion is achieved by the use of an electric motor and the construction is quite similar to that of an automobile engine.
The piston moves up and down inside a cylinder. Vapor from the suction line is moved through the intake valve as the piston move downward. As the piston moves upward, it compresses the vapor refrigerant which is then pushed through the exhaust valve into the condenser.
The compressor may has more than one cylinder which is also known as multi-cylinder compressor. The common ones are the two-cylinder, four-cylinder and eight-cylinder compressors
Scroll
A scroll compressor has one fixed scroll which remains stationary and another moving or orbiting scroll that rotates through the use of swing link. When this happens, the pockets of refrigerant between the two scroll are slowly pushed to the center of the two scrolls causing the reduction of the volume of the gas. It is then discharged though the center port to the condenser.
The advantage of scroll compressor is that it has fewer moving parts and less torque variation compared to the reciprocating compressor. This advantage is translated to a smooth and quiet operation.
The advantage of scroll compressor is that it has fewer moving parts and less torque variation compared to the reciprocating compressor. This advantage is translated to a smooth and quiet operation.
The scroll compressor is also known as scroll pump or scroll vacuum pump.
Screw
Screw
The screw compressor uses a pair of helical rotors where it traps and compresses the gas as the rotors revolve in the cylinder. In HVAC,
they are usually used in systems with 20 ton capacity and above. The male rotor and the female rotor are built inside the cylinder. The low pressure refrigerant enters one end of the compressor and the resultant high pressure refrigerant is discharged into the opposite end to the condenser.
Rotary
The rotary compressor can be divided into two types. One has blades or vanes that rotate with the shaft. The other type has the blade which remains stationary and is part of the compressor housing assembly. In both types, the vapor from the suction line is drawn into the cylinder through the suction port.

As the blade rotates, trapped vapor in the space ahead of the blade is compressed into high pressure gas after which it is discharged to the condenser through the exhaust port. The number of blades can range from two to eight in a single system.
Centrifugal
Centrifugal compressor is usually used in large capacity refrigerating system. In this compressor, the vapor is moved in a circular motion known as centrifugal force. An impeller which is a disk with radial blades spins rapidly inside this housing causing the gas to gain velocity.
A diffuser converts this energy into pressure energy and is then discharged into the condenser. The pumping efficiency increases with speed, hence this type of compressors are designed to operate at high speed.
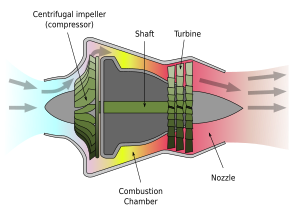
The main advantage of centrifugal compressor is that there are no valves, pistons or cylinders. The wearing parts that need attention are the main bearings.
A centrifugal compressor is a type of dynamic compressor, or turbo compressor, with a radial design. Unlike displacement compressors that work at a constant flow, dynamic compressors work at a constant pressure and the performance is affected by external conditions such as changes in inlet temperatures
Ventilation
Ventilation:-
Ventilating or ventilation (the V in HVAC) is the process of exchanging or replacing air in any space to provide high indoor air quality which involves temperature control, oxygen replenishment, and removal of moisture, odors, smoke, heat, dust, airborne bacteria, carbon dioxide, and other gases. Ventilation removes unpleasant smells and excessive moisture, introduces outside air, keeps interior building air circulating, and prevents stagnation of the interior air.
Ventilation includes both the exchange of air to the outside as well as circulation of air within the building. It is one of the most important factors for maintaining acceptable indoor air quality in buildings. Methods for ventilating a building may be divided into mechanical/forced and natural types
Monday, September 24, 2018
Thermal expansion valve
A thermal expansion valve is a component in refrigeration and air conditioning systems that controls the amount of refrigerant released into the evaporator thereby controlling superheat. Thermal expansion valves are often referred to generically as "metering devices"
DDC
Direct Digital control
Direct Digital control (DDC) is the automated control of a condition or process by a digital device (computer). DDC takes a centralized network-oriented approach. All instrumentation is gathered by various analog and digital converters which use the network to transport these signals to the central controller.
Sunday, September 23, 2018
Refrigerant dangerous
Freon is a tasteless, mostly odorless gas. When it is deeply inhaled, it can cut off vital oxygen to your cells and lungs. Limited exposure — for example, a spill on your skin or breathing near an open container — is only mildly harmful. However, you should try to avoid all contact with these types of chemicals
Saturday, September 22, 2018
Pressure Switch
A high pressure switch (HPS) and a low pressure switch (LPS) are protective devices for the compressor and refrigeration circuit. The high pressure switch monitors the system for an inoperative outdoor motor, and/or a dirty/restricted condenser (outdoor) coil.
A pressure switch is a form of switch that closes an electrical contact when a certain set fluid pressure has been reached on its input. The switch may be designed to make contact either on pressure rise or on pressure fall.
The AC pressure switch is a safety switch that is mounted on both the high and low sides of the air conditioning system. ... Depending on which side of the system the sensor is mounted in, when the pressure rises too high or drops too low, the switch will turn off the compressor to prevent damage from occurring.
High pressure can be caused in a refrigeration plant due to various causes like over charge, loss of cooling water, high ambient temperature, air, or other incompressible gases in the system, and obstruction in the discharge line of the compressor.
The AC pressure switch is a safety switch that is mounted on both the high and low sides of the air conditioning system. It monitors the pressure of the refrigerant on its respective side of the system. ... When the pressure is too low, the compressor risks damage due to running with low oil.
Friday, September 21, 2018
Forced air mean AC
A forced-air central heating system is one which uses air as its heat transfer medium. These systems rely on ductwork, vents, and plenums as means of air distribution, separate from the actual heating and air conditioning systems
Wednesday, September 19, 2018
ACCESSORIES FOR PACKAGE AIR CONDITIONER
FACTORY OPTIONS AND/OR ACCESSORIES FOR PACKAGE AIR CONDITIONER
Economizer (dry--bulb or enthalpy)
Economizers save money. They bring in fresh, outside air
for ventilation; and provide cool, outside air to cool your
building. This is the preferred method of low--ambient
cooling. When coupled to CO2 sensors, economizers can
provide even more savings by coupling the ventilation air
to only that amount required.
Economizers are available, installed and tested by the
factory, with either enthalpy or dry--bulb temperature
inputs. There are also models for electromechanical as
well as direct digital controllers. Additional sensors are
available as accessories to optimize the economizers.
Economizers include gravity controlled, barometric relief
equalizes building pressure and ambient air pressures.
This can be a cast effective solution to prevent building
pressurization.
CO2 Sensor
Improves productivity and saves money by working with
the economizer to intake only the correct amount of
outside air for ventilation. As occupants fill your building,
the CO2 sensor detects their presence through increasing
CO2 levels, and opens the economizer appropriately.
When the occupants leave, the CO2 levels decrease, and
the sensor appropriately closes the economizer. This
intelligent control of the ventilation air, called Demand
Control Ventilation (DCV) reduces the overall load on the
rooftop, saving money.
Smoke Detectors
Trust the experts. Smoke detectors make your application
safer and your job easier. Carrier smoke detectors
immediately shut down the rooftop unit when smoke is
detected. They are available, installed by the factory, for
supply air, return air, or both.
Louvered Hail Guards
Sleek, louvered panels protect the condenser coil from
hail damage, foreign objects, and incidental contact.
Convenience Outlet (powered or un--powered)
Reduce service and/or installation costs by including a
convenience outlet in your specification. Carrier will
install this service feature at our factory. Provides a
convenient, 15 amp, 115v GFCI receptacle with “Wet in
Use” cover. The “powered” option allows the installer to
power the outlet from the line side of the disconnect or
load side as required by code. The “unpowered” option is
to be powered from a separate 115/120v power source.
Non--fused Disconnect
This OSHA--compliant, factory--installed, safety switch
allows a service technician to locally secure power to the
rooftop.
Power Exhaust with Barometric Relief
Superior internal building pressure control. This
field--installed accessory may eliminate the need for
costly, external pressure control fans.
PremierLinkt, DDC Controller
This CCN controller regulates your rooftop’s performance
to tighter tolerances and expanded limits, as well as
facilitates zoning systems and digital accessories. It also
unites your Carrier HVAC equipment together on one,
coherent CCN network. The PremierLink can be
factory--installed, or easily field--installed.
RTU Open, Multi--Protocol Controller
Connect the rooftop to an existing BAS without needing
complicated translators or adapter modules using the RTU
Open controller. This new controller speaks the 4 most
common building automation system languages (Bacnet,
Modbus, N2, and Lonworks). Use this controller when
you have an existing BAS. Besides the 4 protocols, it also
communicates with a Carrier Open system (I--Vu and
VVT).
Time Guard II Control Circuit
This accessory protects your compressor by preventing
short--cycling in the event of some other failure, prevents
the compressor from restarting for 30 seconds after
stopping. Not required with PremierLink, RTU Open, or
authorized commercial thermostats.
Motorized 2--Position Damper
The new Carrier 2--position, motorized outdoor air damper
admits up to 100% outside air. Using reliable, gear--driven
technology, the 2--position damper opens to allow
ventilation air and closes when the rooftop stops, stopping
unwanted infiltration.
Manual OA Damper
Manual outdoor air dampers are an economical way to
bring in ventilation air. The dampers are available in 25%
and 50% versions.
Optional Humidi--MiZer Adaptive
Dehumidification System
Carrier’s Humidi--MiZer adaptive dehumidification
system is an all--inclusive factory installed option that can
be ordered with any rooftop unit.
This system expands the envelope of operation of
Carrier’s WeatherMaster rooftop products to provide
unprecedented flexibility to meet year round comfort
conditions.
The Humidi--MiZer adaptive dehumidification system has
the industry’s only dual dehumidification mode setting.
The Humidi--MiZer system includes two new modes of
operation.
Optional Humidi--MiZer Adaptive
Dehumidification System
rooftop coupled with the
Humidi--MiZer system is capable of operating in normal
design cooling mode, subcooling mode, and hot gas reheat
mode. Normal design cooling mode is when the unit will
operate under its normal sequence of operation by cycling
compressors to maintain comfort conditions.
Subcooling mode will operate to satisfy part load type
conditions when the space requires combined sensible and
a higher proportion of latent load control. Hot Gas Reheat
mode will operate when outdoor temperatures diminish
and the need for latent capacity is required for sole
humidity control. Hot Gas Reheat mode will provide
neutral air for maximum dehumidification operation.
Hinged Access Panels
Allows access to unit’s major components with
specifically designed hinged access panels. Panels are:
filter, control box, fan motor and compressor.
Motormaster Head Pressure Controller
The Motormaster motor controller is a low ambient, head
pressure controller kit that is designed to maintain the
unit’s condenser head pressure during periods of low
ambient cooling operation. This device should be used as
an alternative to economizer free cooling not when
economizer usage is either not appropriate or desired. The
Motormaster will either cycle the outdoor--fan motors or
operate them at reduced speed to maintain the unit
operation, depending on the model.
Winter Start Kit
The winter start kit by Carrier extends the low ambient
limit of your rooftop to 25_F (--4_C). The kit bypasses the
low pressure switch, preventing nuisance tripping of the
low pressure switch. Other low ambient precautions may
still be prudent.
Propane Heating
Convert your gas heat rooftop from standard natural gas
operation to Propane using this field--installed kit.
High Altitude Heating
High altitudes have less oxygen, which means heat
exchangers need less fuel. The new gas orifices in this
field--installed kit make the necessary adjustment for high
altitude applications. They restore the optimal fuel to air
mixture and maintain healthy combustion at altitudes
above 2000 ft (610m). Kits may not be required in all
areas.
Flue Discharge Deflector
The flue discharge deflector is a useful accessory when
flue gas recirculation is a concern. By venting the flue
discharge upwards, the deflector minimizes the chance for
a neighboring unit to intake the flue exhaust (04--12
models only).
Optional Stainless Steel Heat Exchanger
The stainless steel heat exchanger option provides the
tubular heat exchanger be made out of a minimum 20
gauge type 409 stainless steel for applications where the
mixed air to the heat exchanger is expected to drop below
45_F (7_C). Stainless steel may be specified on
applications where the presence of airborne contaminants
require its use (applications such as paper mills) or in area
with very high outdoor humidity that may result in severe
condensation in the heat exchanger during cooling
operation.
Flue Discharge Heat Shield
The flue discharge heat shield keeps people from touching
the rooftop unit’s potentially hot flue discharge. This is
especially useful for ground level applications, where
more, untrained people could have access to the unit’s
exterior (04--12 models only).
Alternate Motors and Drives
Some applications need larger horsepower motors, some
need more airflow, and some need both. Regardless of the
case, your Carrier expert has a factory installed
combination to meet your application. A wide selection of
motors and pulleys (drives) are available, factory
installed, to handle nearly any application.
Thru--the--Base Connections
Thru--the--base connections, available as either an
accessory or as a factory option, are necessary to ensure
proper connection and seal when routing wire and piping
through the rooftop’s basepan and curb. These couplings
eliminate roof penetration and should be considered for
gas lines, main power lines, as well as control power.
Economizer (dry--bulb or enthalpy)
Economizers save money. They bring in fresh, outside air
for ventilation; and provide cool, outside air to cool your
building. This is the preferred method of low--ambient
cooling. When coupled to CO2 sensors, economizers can
provide even more savings by coupling the ventilation air
to only that amount required.
Economizers are available, installed and tested by the
factory, with either enthalpy or dry--bulb temperature
inputs. There are also models for electromechanical as
well as direct digital controllers. Additional sensors are
available as accessories to optimize the economizers.
Economizers include gravity controlled, barometric relief
equalizes building pressure and ambient air pressures.
This can be a cast effective solution to prevent building
pressurization.
CO2 Sensor
Improves productivity and saves money by working with
the economizer to intake only the correct amount of
outside air for ventilation. As occupants fill your building,
the CO2 sensor detects their presence through increasing
CO2 levels, and opens the economizer appropriately.
When the occupants leave, the CO2 levels decrease, and
the sensor appropriately closes the economizer. This
intelligent control of the ventilation air, called Demand
Control Ventilation (DCV) reduces the overall load on the
rooftop, saving money.
Smoke Detectors
Trust the experts. Smoke detectors make your application
safer and your job easier. Carrier smoke detectors
immediately shut down the rooftop unit when smoke is
detected. They are available, installed by the factory, for
supply air, return air, or both.
Louvered Hail Guards
Sleek, louvered panels protect the condenser coil from
hail damage, foreign objects, and incidental contact.
Convenience Outlet (powered or un--powered)
Reduce service and/or installation costs by including a
convenience outlet in your specification. Carrier will
install this service feature at our factory. Provides a
convenient, 15 amp, 115v GFCI receptacle with “Wet in
Use” cover. The “powered” option allows the installer to
power the outlet from the line side of the disconnect or
load side as required by code. The “unpowered” option is
to be powered from a separate 115/120v power source.
Non--fused Disconnect
This OSHA--compliant, factory--installed, safety switch
allows a service technician to locally secure power to the
rooftop.
Power Exhaust with Barometric Relief
Superior internal building pressure control. This
field--installed accessory may eliminate the need for
costly, external pressure control fans.
PremierLinkt, DDC Controller
This CCN controller regulates your rooftop’s performance
to tighter tolerances and expanded limits, as well as
facilitates zoning systems and digital accessories. It also
unites your Carrier HVAC equipment together on one,
coherent CCN network. The PremierLink can be
factory--installed, or easily field--installed.
RTU Open, Multi--Protocol Controller
Connect the rooftop to an existing BAS without needing
complicated translators or adapter modules using the RTU
Open controller. This new controller speaks the 4 most
common building automation system languages (Bacnet,
Modbus, N2, and Lonworks). Use this controller when
you have an existing BAS. Besides the 4 protocols, it also
communicates with a Carrier Open system (I--Vu and
VVT).
Time Guard II Control Circuit
This accessory protects your compressor by preventing
short--cycling in the event of some other failure, prevents
the compressor from restarting for 30 seconds after
stopping. Not required with PremierLink, RTU Open, or
authorized commercial thermostats.
Motorized 2--Position Damper
The new Carrier 2--position, motorized outdoor air damper
admits up to 100% outside air. Using reliable, gear--driven
technology, the 2--position damper opens to allow
ventilation air and closes when the rooftop stops, stopping
unwanted infiltration.
Manual OA Damper
Manual outdoor air dampers are an economical way to
bring in ventilation air. The dampers are available in 25%
and 50% versions.
Optional Humidi--MiZer Adaptive
Dehumidification System
Carrier’s Humidi--MiZer adaptive dehumidification
system is an all--inclusive factory installed option that can
be ordered with any rooftop unit.
This system expands the envelope of operation of
Carrier’s WeatherMaster rooftop products to provide
unprecedented flexibility to meet year round comfort
conditions.
The Humidi--MiZer adaptive dehumidification system has
the industry’s only dual dehumidification mode setting.
The Humidi--MiZer system includes two new modes of
operation.
Optional Humidi--MiZer Adaptive
Dehumidification System
rooftop coupled with the
Humidi--MiZer system is capable of operating in normal
design cooling mode, subcooling mode, and hot gas reheat
mode. Normal design cooling mode is when the unit will
operate under its normal sequence of operation by cycling
compressors to maintain comfort conditions.
Subcooling mode will operate to satisfy part load type
conditions when the space requires combined sensible and
a higher proportion of latent load control. Hot Gas Reheat
mode will operate when outdoor temperatures diminish
and the need for latent capacity is required for sole
humidity control. Hot Gas Reheat mode will provide
neutral air for maximum dehumidification operation.
Hinged Access Panels
Allows access to unit’s major components with
specifically designed hinged access panels. Panels are:
filter, control box, fan motor and compressor.
Motormaster Head Pressure Controller
The Motormaster motor controller is a low ambient, head
pressure controller kit that is designed to maintain the
unit’s condenser head pressure during periods of low
ambient cooling operation. This device should be used as
an alternative to economizer free cooling not when
economizer usage is either not appropriate or desired. The
Motormaster will either cycle the outdoor--fan motors or
operate them at reduced speed to maintain the unit
operation, depending on the model.
Winter Start Kit
The winter start kit by Carrier extends the low ambient
limit of your rooftop to 25_F (--4_C). The kit bypasses the
low pressure switch, preventing nuisance tripping of the
low pressure switch. Other low ambient precautions may
still be prudent.
Propane Heating
Convert your gas heat rooftop from standard natural gas
operation to Propane using this field--installed kit.
High Altitude Heating
High altitudes have less oxygen, which means heat
exchangers need less fuel. The new gas orifices in this
field--installed kit make the necessary adjustment for high
altitude applications. They restore the optimal fuel to air
mixture and maintain healthy combustion at altitudes
above 2000 ft (610m). Kits may not be required in all
areas.
Flue Discharge Deflector
The flue discharge deflector is a useful accessory when
flue gas recirculation is a concern. By venting the flue
discharge upwards, the deflector minimizes the chance for
a neighboring unit to intake the flue exhaust (04--12
models only).
Optional Stainless Steel Heat Exchanger
The stainless steel heat exchanger option provides the
tubular heat exchanger be made out of a minimum 20
gauge type 409 stainless steel for applications where the
mixed air to the heat exchanger is expected to drop below
45_F (7_C). Stainless steel may be specified on
applications where the presence of airborne contaminants
require its use (applications such as paper mills) or in area
with very high outdoor humidity that may result in severe
condensation in the heat exchanger during cooling
operation.
Flue Discharge Heat Shield
The flue discharge heat shield keeps people from touching
the rooftop unit’s potentially hot flue discharge. This is
especially useful for ground level applications, where
more, untrained people could have access to the unit’s
exterior (04--12 models only).
Alternate Motors and Drives
Some applications need larger horsepower motors, some
need more airflow, and some need both. Regardless of the
case, your Carrier expert has a factory installed
combination to meet your application. A wide selection of
motors and pulleys (drives) are available, factory
installed, to handle nearly any application.
Thru--the--Base Connections
Thru--the--base connections, available as either an
accessory or as a factory option, are necessary to ensure
proper connection and seal when routing wire and piping
through the rooftop’s basepan and curb. These couplings
eliminate roof penetration and should be considered for
gas lines, main power lines, as well as control power.
AC thermistor
An AC thermistor is a type of temperature sensor that is commonly found on modern AC systems. They detect temperatures and send a resistance signal to the AC control module so that the automatic adjustments can be made to keep the cabin at the correct temperature.

Condensing temperature
The condensing temperature is the temperature at which a cooling medium changes phases from a gas to a liquid. When this phase change occurs, the cooling medium condenses. The temperature at which a cooling medium condenses is dependent on the type of coolant and the condensing pressure.
Evaporator and Condenser Difference
While the evaporator coil picks up heat from indoor air, the condenser coil releases heat into outdoor air. The load of heat energy extracted from your home and compressed in hot refrigerant vapor is rapidly released when refrigerant circulates into the coil and condenses to liquid.
Expansion Valve
Expansion Valve. The expansion valve removes pressure from the liquid refrigerant to allow expansion or change of state from a liquid to a vapor in the evaporator. ... Under a greatly reduced pressure the liquid refrigerant is at its coldest as it leaves the expansion valve and enters the evaporator.

Tuesday, September 18, 2018
HVAC Principle
its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC System Design is a sub discipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics and heat transfer. ... Methods for ventilating a building may be divided into mechanical/forced and natural types.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
air cooled and water cooled chiller difference
Air cooled and water cooled chiller difference Air Cooled Chiller . Both air - cooled and water - cooled chillers depend on an air ...

-
There are 2 types of Central air conditioning systems : 1. Direct Expansion (DX) type of central air condition plants 2. Chi...
-
Sensible Heat The sensible heat in a heating or cooling process of air (heating or cooling capacity) can be calculated in SI-unit...
-
A high pressure switch (HPS) and a low pressure switch (LPS) are protective devices for the compressor and refrigeration circuit. The hi...